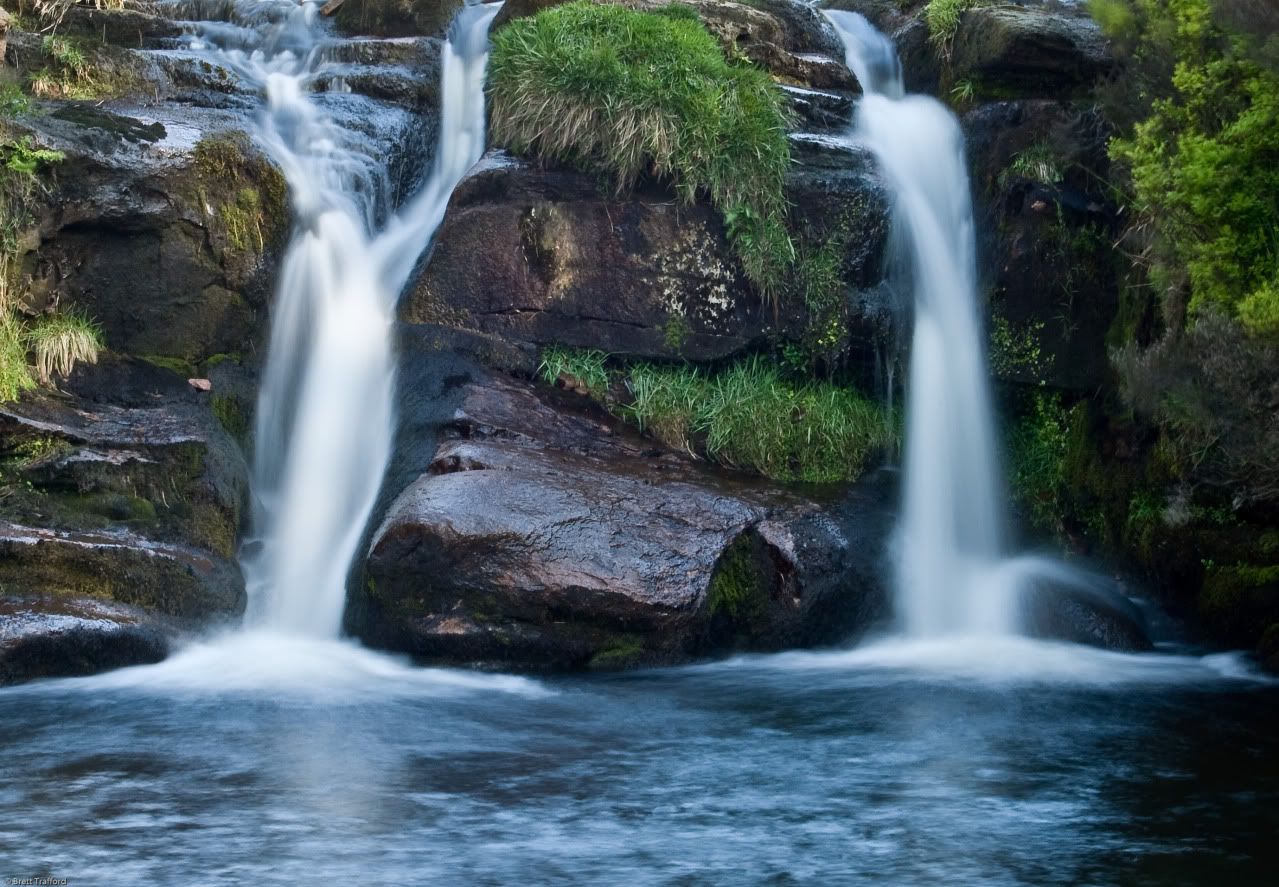
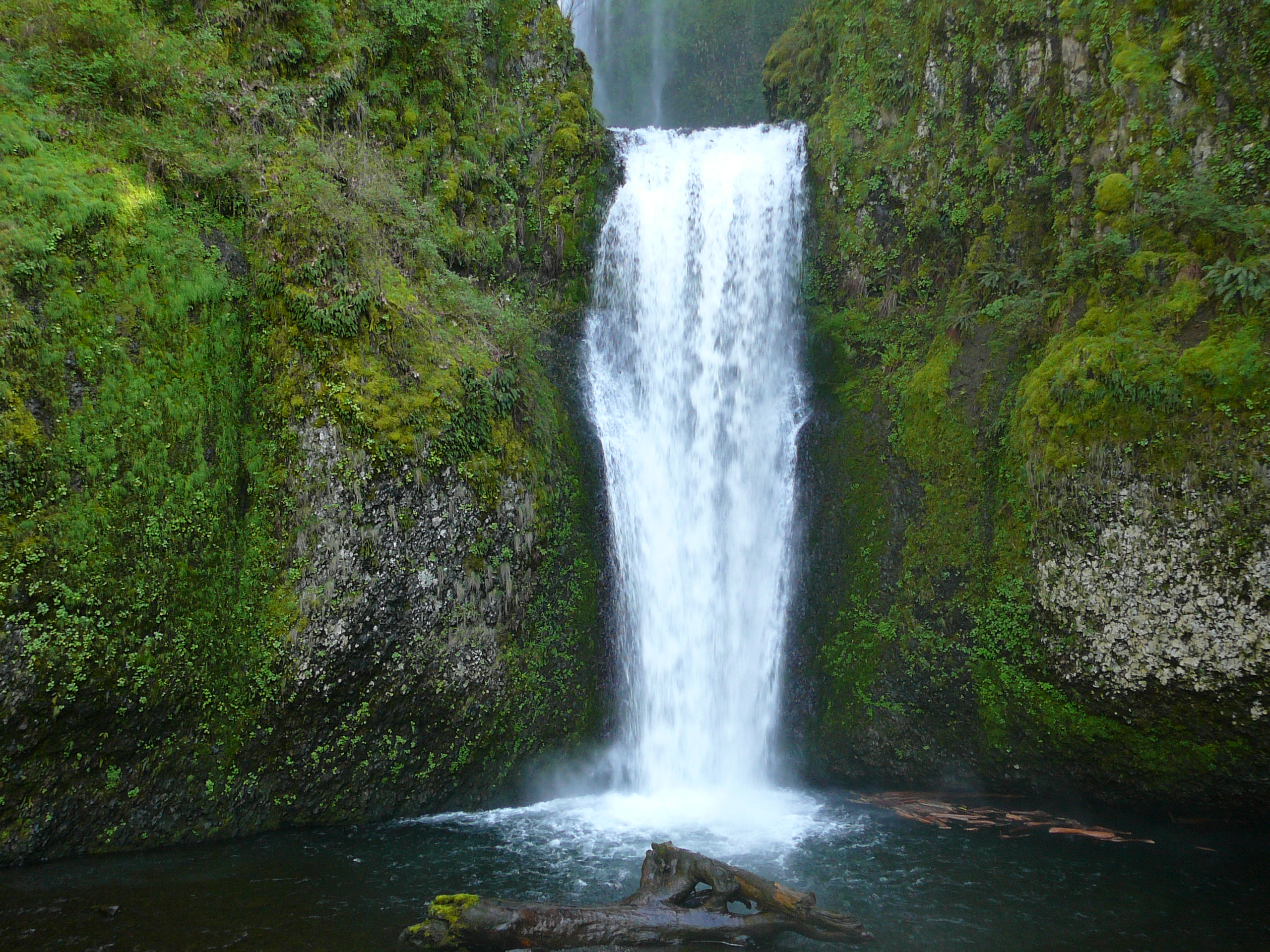
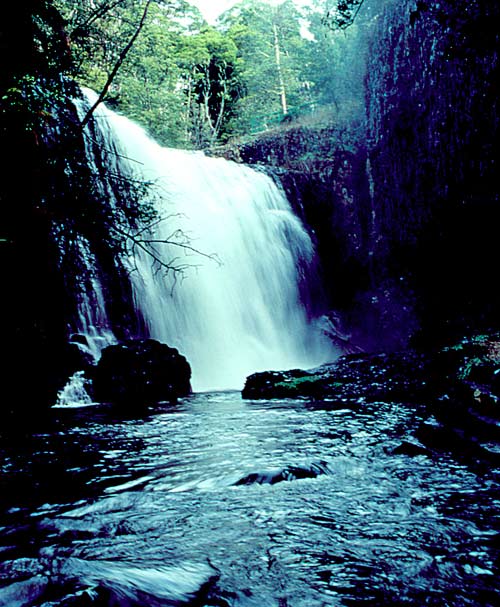
"A waterfall is a place where water flows over a vertical drop in the course of a river or stream." (wiki)
The formation of Waterfalls
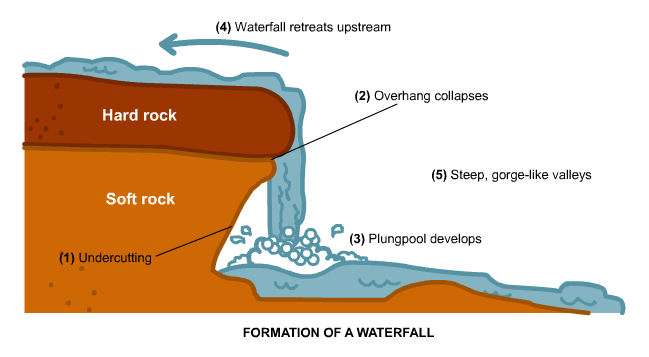
1.Waterfalls are found in the upper course of a river. They usually occur where a band of hard rock lies next to soft rock. They may often start as rapids.
2. As the river passes over the hard rock, the soft rock below is eroded (worn away) more quickly than the hard rock leaving the hard rock elevated above the stream bed below.
3.
The 'step' in the river bed continues to develop as the river flows
over the hard rock step (Cap Rock) as a vertical drop.
4.
The drop gets steeper as the river erodes the soft rock beneath by
processes such as abrasion and hydraulic action. A plunge
pool forms at the base of the waterfall.5. This erosion gradually undercuts the hard rock and the plunge pool gets bigger due to further hydraulic action and abrasion.Eventually the hard cap rock is unsupported and collapses. The rocks that fall into the plunge pool will continue to enlarge it by abrasion as they are swirled around. A steep sided valley known as a gorge is left behind and as the process continues the waterfall gradually retreats upstream.
(source)
Types of waterfalls
- Block: Water descends from a relatively wide stream or river.
- Cascade: Water descends a series of rock steps.
- Cataract: A large, powerful waterfall.
- Chute: A large quantity of water forced through a narrow, vertical passage.
- Fan: Water spreads horizontally as it descends while remaining in contact with bedrock.
- Frozen: Any waterfall which has some element of ice.
- Horsetail: Descending water maintains some contact with bedrock.
- Plunge: Water descends vertically, losing contact with the bedrock surface.
- Punchbowl: Water descends in a constricted form and then spreads out in a wider pool.
- Segmented: Distinctly separate flows of water form as it descends.
- Tiered: Water drops in a series of distinct steps or falls.
- Multi-step: A series of waterfalls one after another of roughly the same size each with its own sunken plunge pool.
(source)
(source)
(source)
(source)
This isn't a waterfall environment, but studying cliffs is a good idea too.
NOTE:
- Main mass of land is on level of river, not the bottom of the waterfall.
- From above, will need to set height limit higher
- Mostly rock, possibly covered in moss or some vegetation on sides
- Make big boulder looking things
- Sides should be rock, not grass
(source)
Looking at Frank Lloyd Wright's Fallingwater House is unavoidable.
Building on top of a waterfall is not really feasible because of errosion. Wright would have gone to great lengths to ensure the longevity of his design.
The meeting space between the two monuments acts as a bridge over the water, and the movement is visible through the void.
(source)
(source)
(source)
(source)
The bridges are never placed very close to the waterfalls, partially because of erosion and partially because of noise and water splashing... In short, no one wants to be that close to a waterfall. For this exercise, I think I will forgo practicality for effect. :)












No comments:
Post a Comment